The Drift Eliminator is a trap for trapping water droplets sucked into the air outlet of the cooling tower. The main function of this part is to prevent water droplets from drifting or being thrown towards the suction fan. The word Drift Eliminator in English consists of two main parts. The first part of the word (Drift) means throwing tiny water droplets from the outlet of the cooling tower nozzle towards the fan and the second part of the word (Eliminator) means preventing.
Types of drip eliminator applications
In addition to being used in cooling towers, drip eliminators are also used in various air washers and evaporative condensers. Due to its protective role, it is considered one of the most important peripheral parts of the cooling tower. The eliminator or drip eliminator is placed between the water spray system and the air outlet in the cooling tower or air washer, either vertically (flat) or horizontally (standing). In order to increase the efficiency of the drip eliminator, in some cases, two or more layers of drip eliminators are generally used to prevent water droplets from escaping.
The standard height of the drippers used in cooling towers and air washers varies between 13 and 20 cm and varies according to the type of dripper (honeycomb or blade). The amount of drift or throwing of water droplets towards the impeller is not important in terms of energy consumption (water consumption).
The use of an air outlet eliminator in devices that deal with water spraying mostly serves to protect the components of the aeration system (such as a cooling tower). Some of these components of the aeration system include: the motor, the cooling tower fan, and the power transmission system.
How a cooling tower dripper works
The impeller or fan in the cooling tower sucks the air flow upward from the louver (air inlet shutter) at a certain pressure. By doing this, a small rate of fine droplets from the cooling tower nozzle outlet are directed towards the upper outlet (fan deck) due to the suction force of the impeller.
These tiny water droplets lose their kinetic energy when they hit the cooling tower’s drip catcher plates and blades (they get trapped) and return downwards due to the force of gravity. Simply put, the cooling tower drip catcher is a kind of trap in the path of the water droplets sucked towards the impeller, which prevents these small and macroscopic water droplets from drifting out.
Application and location of cooling tower drip catcher
Drip catcher or drip catcher is used in various types of cubic and conical (open circuit) cooling towers, as well as in various capacities of hybrid closed circuit cooling towers. In addition to cooling towers, this equipment is also used in various types of air washers, and its purpose is to prevent droplets and water vapor from passing outside the device.
The drip catcher creates a contact surface that causes condensation or dew on some of the droplets and moisture in the air, and is therefore also called a dew catcher. The importance of the drip catcher is mainly due to its direct impact on the water consumption of the cooling tower and air washer. Incidentally, in order to reduce the water consumption in cooling tower calculations, the use of a drip catcher or dew catcher is highly recommended.

In a cubic cooling tower, the drip eliminator is located at the top of the nozzle, before the fan stack. The droplets exiting the nozzle in a cubic cooling tower are returned downward by the drip eliminator. In a conical cooling tower, the drip eliminator or eliminator is located at the top of the water outlet pipes of the cooling tower diffuser and is attached to the pipe by a clamp.
The water droplets and vapors exiting the holes of the rotating water spray system are deflected downward after hitting this type of drip eliminator. In a colloquial term, a conical or circular cooling tower drip eliminator is also called an eliminator for short.
Cooling tower dripper material
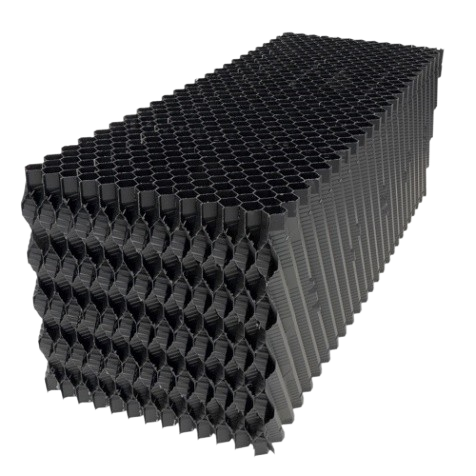
Types of cubic cooling tower drippers are produced and supplied in two types: honeycomb or cellular and blade type. Due to the constant contact of the cooling tower dripper or dew catcher with the humid air flow and water droplets, this equipment is generally produced from polymer materials. The main material of the cooling tower dripper is generally either PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or in some types, PP (polypropylene) material is used in the production and design of the dripper.
The conical cooling tower eliminator or drip catcher is also generally manufactured from two materials: PP and FRP fiberglass. All three materials, PVC, PP, and FRP, have good resistance to sediment, corrosion, and decay in water, and in fact, this is the main reason for choosing these three grades of materials in the construction of cooling tower drip catcher.
Blade and honeycomb drippers are produced by an extruder (continuous injection and molding) and then assembled with special granule adhesive and spacers. Blade drippers are extruded to specific lengths and then placed next to each other with 10 and 12 spacers.
The width created by each complete set of blade drippers is equivalent to a width of 33 cm, which is coiled together in a male and female manner. The injection of blade-shaped sheets of blade drippers is adjusted to a thickness between 500 and 800 microns, and the sheets produced are produced and supplied in single-hump and double-hump forms.
The granule grade used in blade drippers is made of copolymer grade polypropylene material with the highest transparency and impact resistance, which is melted and formed into sinusoidal sheets at temperatures between 150 and 200 degrees Celsius.
The PVC granule grade used in the injection molding of honeycomb drip block molds comes in various grades in black, gray, and white. Lighter PVC grades are more flexible and resistant than darker grades.
Advantages of using drip catcher in cooling towers
- Preventing excessive water consumption by drifting or throwing drops into the drip catcher
- Preventing droplets from entering the fan and damaging the impeller, motor, and cooling tower ventilation system
- Increasing the life of aeration system components by reducing drift in the cooling tower
- Reducing TDS by reducing the amount of water thrown into the cooling tower
- No sedimentation and corrosion in the presence of water and humidity in the air
- High resistance to sunburn and UV radiation in polypropylene grade
- High resistance to acid washing and acid vapors in the air (scrubber)